Best Way to Learn Dutch According to Research
Determining the best way to learn Dutch can be difficult because every learner has a different learning style and there are different ways of learning Dutch. What works for some people, may not necessarily work for you. To determine the best way to learn Dutch for you, I’m going to share with you effective strategies to learn Dutch based on research. In this way, you’ll get both objective viewpoints about how best to learn Dutch.
Ways of Learning Dutch
There are two main ways to learn Dutch. The first is in a classroom or one-on-one environment. This can be in a school, private tutoring or studied at a college. This method is often structured in a traditional format and is based on the teacher’s own curriculum and method.
The second way of learning Dutch is through self-taught methods such as using Anki flashcards, books and cultural immersion (living aboard). This method is fluid and adaptable to your own learning style and interests. Since you determine how you learn and what you learn, this method can often be more personalized and reliant on the learner.
These are generally the two main categories of how one can learn Dutch. Often you may use one or even both methods throughout your language learning journey. But what makes these methods effective and how do we then determine what is the best way to learn Dutch?
What Does Scientific Research Say About the Best Way to Learn Dutch?
The first logical step is to look at what the scientific research tells us about learning a foreign language. Academic researchers and linguists have already done decades of research studies that examine the best way to learn a second language. These studies can help guide us in determining the best method for learning Dutch. Rather than randomly guessing or making up our own methods from scratch without reputable and proven results, we should look at what already works according to the research. Then, we can focus on implementing the lessons from the research to learn Dutch.
Theory of Second Language Acquisition
Stephen Krashen is a renowned academic researcher from the University of Southern California, United States. He specializes in the study of second language acquisition and has published over 100 books and articles on the topic. He has done several studies that analyze the best way to learn another language. In particular, Stephen Krashen is known for his theory of second language acquisition, which consists of five main hypotheses:
- Acquisition-Learning hypothesis
- Monitor hypothesis
- Input hypothesis
- Affective Filter hypothesis
- Natural Order hypothesis
The most important of these is the “Input Hypothesis”. So, let’s talk in-depth about the Input hypothesis because it can help us determine the best way to learn Dutch, based on Krashen’s research. The Input hypothesis is the concept of input-based learning. In Stephen Krashen’s own words, “acquisition requires meaningful interaction in the target language – natural communication – in which speakers are concerned not with the form of their utterances but with the messages they are conveying and understanding… ‘comprehensible input’ is the crucial and necessary ingredient for the acquisition of language.”
What does this mean? Input can be in the form of books, movies, newspapers, websites, TV shows and anything else that a Dutch learner can listen or read in Dutch. While input-based language learning is all about getting as much comprehensible input and exposure of Dutch as possible, particularly when that input is just one step beyond the learner’s current stage in the target language. Comprehensible Input therefore is input that a learner can understand but not necessarily be able to produce.
“The best methods are therefore those that supply ‘comprehensible input’ in low anxiety situations, containing messages that students really want to hear. These methods do not force early production in the second language, but allow students to produce when they are ‘ready’, recognizing that improvement comes from supplying communicative and comprehensible input, and not from forcing and correcting production.”
Stephen Krashen
It is important to note that Krashen believes that input-based learning should be done naturally and not through constant drilling of information. Unlike traditional methods of learning Dutch at school or with a language teacher where we are constantly drilling in grammar points, we should try our best to learn Dutch in more relaxed and natural environments such as immersion or engagement with Dutch that we personally enjoy. Krashen believes that, over time, this will lead to fluency in the second language.
Four Strands of Language Learning
Stephen Krashen put forward the idea that learning should just mainly and only be through input based methods. However, he points out that in order for that input to be effective, it’s important that that input is comprehensible. However, at the beginning stages of learning any language, it can be very difficult to understand anything because you are not yet able to use the grammar structures, the vocab, and even a sense of the pronunciation of that language.
Although Krashen’s research is important for considering how best to learn Dutch, on the other hand, Paul Nation’s research is more of a balanced approach that we prescribe to more. We believe that Paul Nation’s approach is more practical, especially for adult language learners.
Paul Nation is a professor at the Victoria University of Wellington, New Zealand, who is known for his research in the field of language acquisition.
Paul Nation does agree with Krashen that comprehensible input can lead to language proficiency, but it is just one major component of a balanced learning program. He recommends to dedicate time in what is known as the Four Strands approach. The Four Strands approach contains four areas in which language learners should give equal weight to in order to reach fluency.
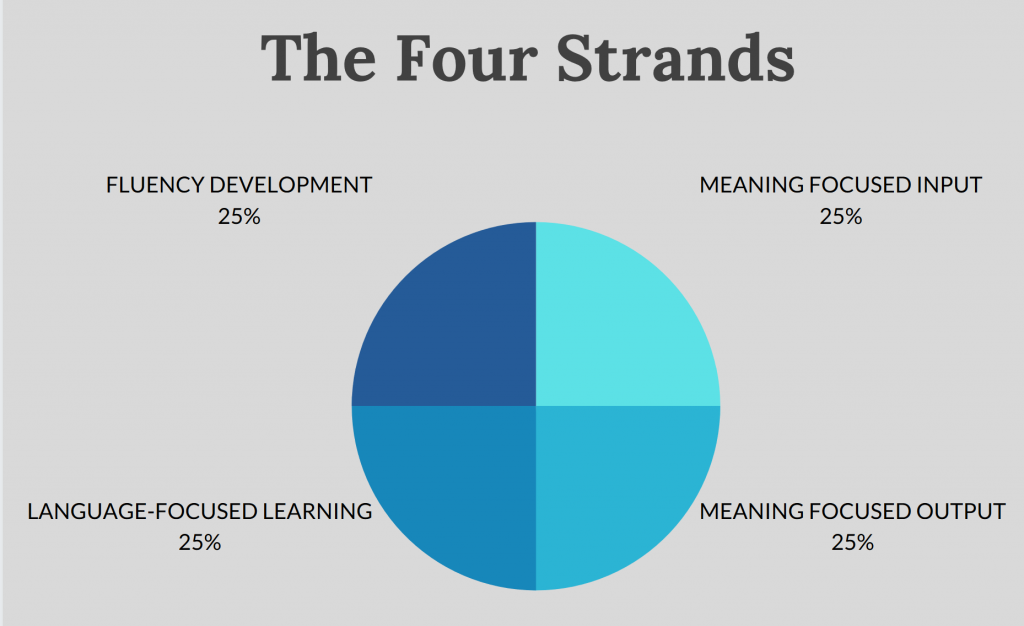
The Four Stands are:
- meaning focused input
- meaning focused output
- language-focused learning
- fluency development
The first strand focuses on input (reading and listening) and this is largely the same as Stephen Krashen’s ideas about the importance of comprehensible input. Paul Nation differs from Krashen in one major area of the Four Strands, namely “language-focused learning”.
In this strand, Paul Nation stresses the need to have some deliberate attention to language features, using tools like flashcards. Language features include spelling, pronunciation, vocabulary, grammar, discourse and multiword units. In order to reach fluency, a learner must also spend time on learning the language features of Dutch.
We largely agree with Paul Nation because we find it can be more effective and efficient for adult language learners to combine both comprehensible input and deliberate attention to some language features using flashcards. Some “language-focused learning” is particularly important for beginner level learners who are not able to comprehend any Dutch yet, so implementing Krashen’s input hypothesis would be very difficult at the beginner and low-intermediate levels.
Retaining Dutch in Your Long-Term Memory
While Paul Nation argued that flashcards can be useful for language-focused learning, he never analyzed in-depth about the best types of flashcards to use. He also never really examined how to use them effectively so you can memorize everything you learn in Dutch. So, that’s why we’re going to bridge that gap. Let’s go into more detail about how to use flashcards as a powerful tool to help you learn the basic language features of Dutch.
If you want to speak Dutch your brain has to be working with completely different concepts, breaking down the words in different concepts and manipulating these concepts in a totally different way. As a result, if you want to be fluent you can’t just have English thoughts and directly translate them into Dutch. You have to be thinking in Dutch at first instance, which means you have to completely rewire your brain. It’s like adding a new operating system, an entirely new way of functioning of your brain. This can be difficult to do, especially if you have thousands of nuances and language features to learn in Dutch pronunciation, spelling, vocabulary and grammar.
In addition, if you are a beginner in Dutch, constant input can be difficult to retain because you are unfamiliar with the language. So how can we retain everything that we learn in our long-term memory so that we can think in Dutch and therefore become fluent in Dutch?
This is where Spaced Repetition comes into play. Spaced repetition is an evidence-based learning technique that spaces out your study sessions using timed intervals in order for you to retain the information for a longer period of time.
Spaced repetition is based on the research findings of Hermann Ebbinghaus, a psychologist in the 1880’s. Ebbinghaus specialized in the study of memory through his years of research memorizing lists of nonsensical syllables that he made up. He recorded three important results:
- The amount of times he studied each list
- The time intervals between each session
- How much of the information he was able to recall
From his research, he found that our brains learn more effectively when we space out our learning over time. This led to Hermann Ebbinghaus’ Forgetting Curve. The Forgetting Curve is a graph demonstrating the rate at which memory can fade over time. In order to improve your brain’s ability to recall what you studied, we need to overcome the Forgetting Curve.
We do this through Spaced Repetition. When we think back on the methods of learning Dutch, again, traditional forms of learning Dutch do not take into account the Forgetting Curve and the use of Spaced Repetition, which can make it difficult for a learner to retain Dutch in the long-term. So many beginner Dutch learners often find that they forget the most basic material that they had already covered in the past.
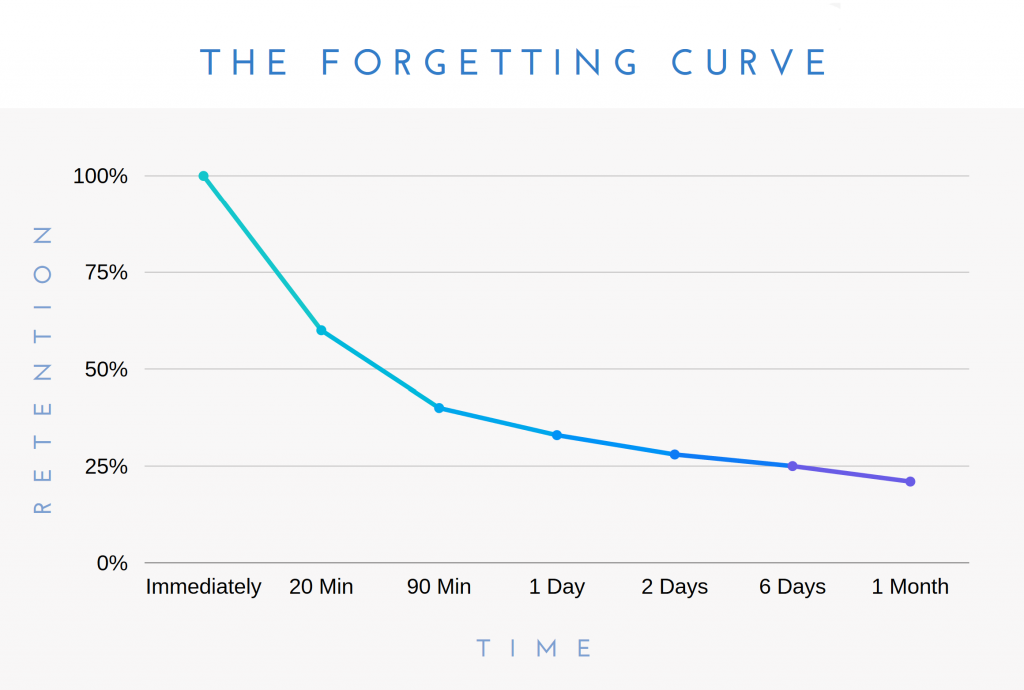
This is where the tool, Anki, can be helpful for you. Anki is a Spaced Repetition flashcards software that uses Ebbinghaus’ spacing effect to space out flashcards over time. Although it is used for other educational purposes, language learners have also found Anki extremely useful to retain a secondary language.
The use of Anki flashcards means that you’ll be able to remember everything you learn. You could use Anki to learn thousands of Dutch words, the basics of Dutch pronunciation and grammar. This will speed up the learning process significantly and when compared to other ways of learning Dutch, it is far more effective.
Best Way to Learn Dutch
Now that we know the essential research that’s out there on language acquisition, we can now look at the steps to learn Dutch from beginner to fluency. We will be trying to integrate what we’ve learned from the research into how we learn Dutch. Again, this is developed from understanding the research and through personal experience of what is already working.
In order to learn Dutch, the best way is to start off with learning pronunciation, vocabulary and grammar. We’ll use what we learned from Paul Nation and use our time to hone in on language-focused learning. We do this through using Spaced Repetition in order to retain all of this new information in our long-term memory. This foundational effort will help us make Dutch input more comprehensible.
As you progress, we’re going to gradually decrease the amount of deliberate practice through flashcards and other pre-made resources, and start to increase the amount of input of natural language materials as recommended by Stephen Krashen’s comprehensible input. This is because the more you advance in Dutch, the more you’ll be able to comprehend Dutch materials. Therefore, you’re more able to simply use the ideas of comprehensible input as a way to continue learning Dutch with greater ease. Let’s look at the steps to learn Dutch.
1. Pronunciation
Dutch pronunciation is key to tackle at the beginning and there are 3 areas that are important to learn.
The Dutch Alphabet
This involves first learning the alphabet of Dutch because the alphabet is the basic building block of the Dutch language. It includes all of the Dutch letters, many of which are similar to English. But there are some that are different and it’s important to learn how to pronounce all them well and how they sound. This will allow you to basically read Dutch words and understand their simple sounds.
Dutch IPA
The Dutch International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) will help you learn how to produce the specific sounds of Dutch with your mouth. The IPA can especially help you with certain Dutch letter combinations that lead to a unique sound. For example, “hoed” ( [hut] ), which means “hat”. If you read this Dutch word as it’s spelled in regular Dutch letters, then you may not pronounce it correctly.
As a native English speaker, you may pronounce it as “ho-ed”, but that is incorrect and a Dutch speaker will be totally confused. You’ll feel embarrassed and not get your point across. But, if you read the IPA of “hoed”, you’ll find it spelled like this ” [hut] “.
.
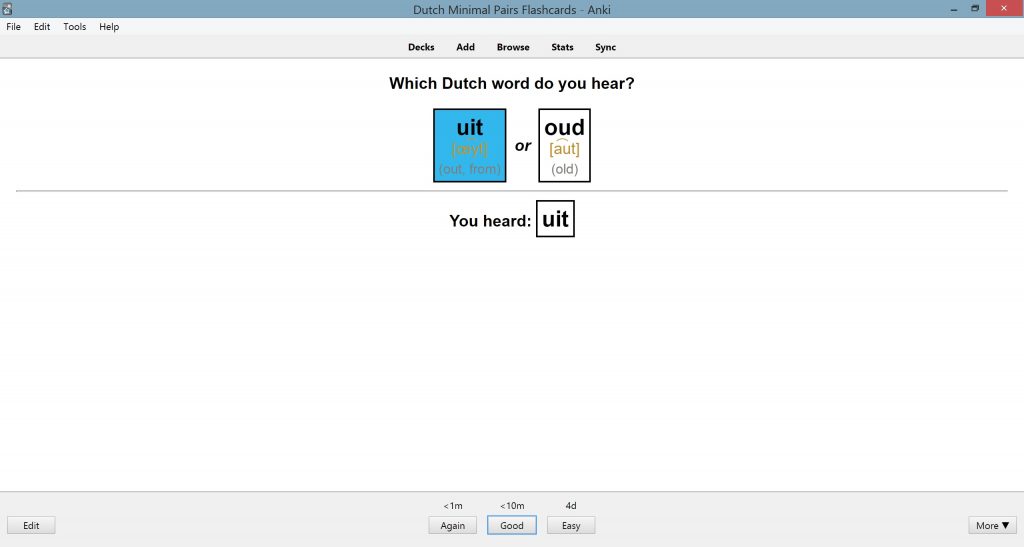
Minimal Pairs
When learning pronunciation, minimal pairs are also useful in order to test your ability to distinguish similar Dutch sounds. There’s also research showing that the use of minimal pairs can be useful to help learners tell the difference between the sounds of Dutch and other languages. For example, you could focus on minimal pairs such as “uit” (from) and “oud” (old), so that you can train your ears to hear the difference. If you can hear the difference between similar Dutch sounds using minimal pairs, this will naturally help you to improve your spoken pronunciation as well since you can better listen to and auto-correct your speech.
Anki is a great way to learn Dutch pronunciation because it can essentially allow you to test your pronunciation and comprehension skills. Anki can help you memorize the alphabet, the IPA sounds, as well as the distinction of the minimal pairs. You can purchase pre-made Anki flashcards for Dutch pronunciation so you can focus on learning rather than making flashcards.
2. Vocabulary
The second step is to learn the basic vocabulary of Dutch. Once you’ve got the sounds and are able to distinguish the unique Dutch sounds, you are now ready to expose yourself to actual words. But which words should you start to learn? As a start, we suggest that you use these 2 criteria when you choose which Dutch words to learn first:
- Words and phrases that are the most frequently used in Dutch
- Words that are easily represented using images
According to research from Paul Nation, and many other linguists, the top 2000 words in any given language including Dutch, represent about 90% of the language that you will encounter in day to day speech. For the sake of efficiency, it makes sense to learn the most frequently used 2000 words and learn any additional words depending on your own interests and encounters.
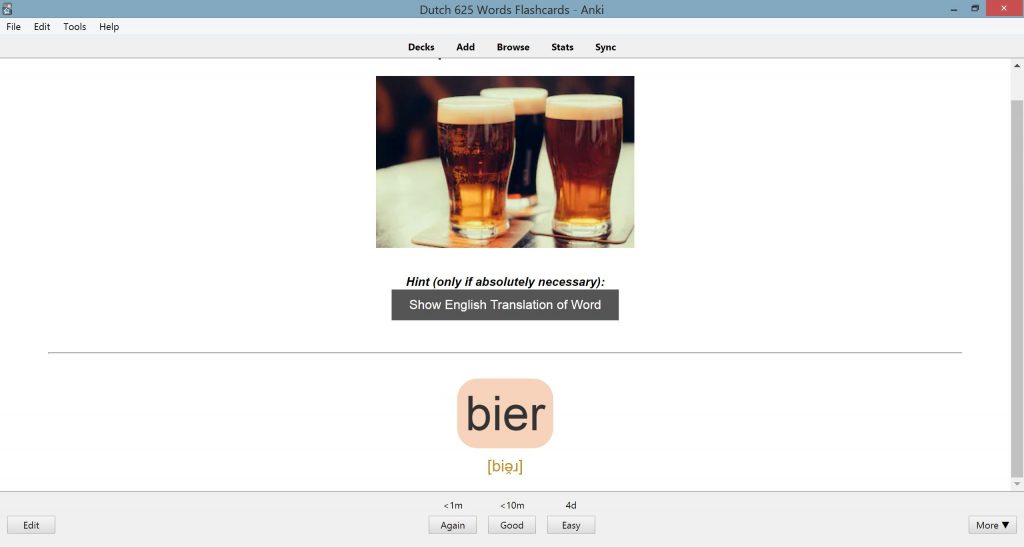
To start off with, you could focus on the most common words that are also picture-based words. Picture-based words are ideal because these are words that are commonly used, but can also be represented with a picture, so they are easier to remember. This is because you can associate a word with an object or image that you may already know in your native language.
For example, the word tree in Dutch is ‘de bier’. If you learn ‘de bier’ by using a picture of a beer, then you’ll be able to quickly think of this cat picture, instead of relying on the English word ‘beer’ to translate to the Dutch word ‘de bier’. What you are doing is learning the direct connection between the representation of the cat and ‘de bier’ so that it’s a lot faster and easier to remember. It’s all about getting familiar with Dutch words for very basic concepts that you already know.
When you have completed picture-based words, you can then move on to basic Dutch phrases. This is really helpful to learn so you can start to speak and ask for basic things in common real life situations. For example, “where’s the train station?”, “Where’s the bathroom?”.
The next step is to cover all the abstract words that may not necessarily be easy to visualize, but are part of the top 2000 words and are commonly used in Dutch. This will help you in your following step, which is learning grammar.
Again, using Anki flashcards in order to learn vocabulary is immensely helpful because it will skip words that you already know or are easy for you. Instead, it will test you on words that you may have difficulties remembering so more of your brain power is focused on words that you need to study. Anki’s Spaced Repetition flashcards software comes in handy for this part because you’ll need to learn and memorize thousands of Dutch words and Anki keeps track of your progress for you.
3. Grammar
The next step is to learn the basics of grammar. This is a way to understand the simple sentence structures of Dutch. If you want to get to a B2 level and actually speak fluently, you’ll really want to mainly focus on grammar points up to the B2 level.
You can do this by going through a Dutch grammar textbook. As you do this, you can add the relevant grammar points in Anki flashcards to help you memorize those grammar points and identify them easily whenever you encounter them in native Dutch content.
Be sure to include full example sentences in your flashcards so that you can understand the grammar points in context. By including Dutch sentence examples in your grammar-based flashcards, you can start getting into comprehensible input and training your brain to think and understand messages all in Dutch.
Similar to learning Dutch pronunciation and vocab, using a pre-made Anki Dutch flashcards deck can be extremely helpful in saving you time and energy making flashcards from scratch.
4. Living the Language
The main purpose of the first three steps is to make Dutch as comprehensible as possible in order to ease you into the final stage which is all about living the language. This is where you’ll really focus on a lot of input, some output as required, and have fun personalizing your Dutch experience.
The bulk of the time should really be focused on finding content that was originally created for native Dutch speakers. Focus on finding content that you like and are interested in, whether it’s songs, movies, books, TV series, even games or just simply chatting to people. The point here is to try and integrate Dutch into your life in a way that is compelling and interesting for you. So that you completely forget about the fact that you’re trying to learn Dutch, but you are actively putting yourself immersed in the Dutch language. Preferably, the content will be just above your current Dutch level so that you can comfortably understand it, but you are constantly pushing yourself to learn a little bit more advanced Dutch every day.
At this stage, using Anki shouldn’t take too much of your time. It is still useful to make new flashcards when you discover new words or grammar points that you’d like to memorize, or there are rare words that you particularly want to remember. A lot of the time should be focused on personalized input that’s meaningful for you and that you can generally understand.
In this step, we’re really honing in on Stephen Krashen’s research on the input hypothesis. We’re increasing the amount of input and interactions with real native Dutch speaking material.
In addition to comprehensible input and language-focused learning at this stage, you may also want to balance it out with output and fluency development activities, as Paul Nation suggests. In particular, you could also focus on and practice speaking Dutch, writing and interacting with native Dutch speakers. The goal would be to improve your accuracy and flow whenever you speak or write Dutch.
In general, the whole point of Step 4 is to find ways to integrate Dutch into your life so you build regular habits of consuming and producing Dutch that’s personally relevant and interesting for you. In this way, Dutch will be a greater part of your life and identity so you will constantly improve your Dutch skills.
The Bottom Line About the Best Way to Learn Dutch
Overall, the best way to learn Dutch, is through comprehensible input over time with language-focused learning as the foundation to kick start your Dutch comprehension. Spaced Repetition is an essential tool to memorizing everything you need to know, especially during the initial language-focused learning stages.
I hope we can help you in your journey to learn Dutch. Again, if you want to learn the best way to learn Dutch, you can sign up here to receive updates on Speakada’s book where we’ll go in-depth about how to learn Dutch and become fluent.
You May Also Like
More Anki Dutch Articles

Best Dutch Anki Decks 2024 That You Need Now

How to Learn Dutch Vocabulary

How to Use Anki for Dutch

Mastering Dutch Made Easy: Step-By-Step Guide for How to Learn Dutch Now

How Long Does It Take to Learn Dutch Now